The Business Case for Energy Storage: Cost Effective Solutions for a Sustainable Future
- 23/12/04
- Energy Storage
With the next phase of Paris Agreement goals rapidly approaching, governments and organisations around the world are looking to increase the adoption of renewable energy sources. Some of the regions with the heaviest use of energy have extra incentives for pursuing alternatives to traditional energy. For example, in Europe, the incentive stems from an energy crisis but in the United States, it comes courtesy of the Inflation Reduction Act, a 2022 law that allocates $370 billion to clean-energy investments.
And according to McKinsey analysis, more than $5 billion was invested in Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) in 2022 which is an almost threefold increase from the previous year. They also expect the global BESS market to reach between $120 billion and $150 billion by 2030, more than double its size today creating a sizable market opportunity for investors.
Driving forces behind energy storage demand
The surge in demand for BESS is largely fueled by the ongoing evolution of energy infrastructure worldwide. As the world continues to shift towards renewable energy sources, the need for efficient energy storage solutions becomes of critical importance. Storage systems like Trina's Elementa are crucial in managing the intermittency of renewable energy, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply.
Local policies play a significant role in this transformation. Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly recognising the importance of modernising the grid to accommodate new energy sources. Incentives and regulations are being implemented to encourage the adoption of BESS, facilitating grid upgrades and transformations. These policies not only support the integration of renewable energy but also enhance the resilience and efficiency of the energy infrastructure.
Globally, the trend towards decarbonisation and sustainable energy practices is accelerating the adoption of BESS. Countries are setting ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, with renewable energy and storage systems at the core of these strategies. This global shift is not just an environmental imperative but also an economic one, as energy storage systems offer a pathway to more efficient and cost-effective energy management, aligning with the global push towards a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.

BESS application and market opportunities
The combination of solar power with energy storage represents a highly viable and beneficial synergy. This pairing addresses a fundamental challenge of solar energy – its variability. By storing excess energy produced during peak sunlight hours, energy storage systems allow for a more consistent and reliable energy supply, even when the sun isn't shining. This not only maximises the utility of solar installations but also enhances grid stability and resilience.
Grid services
The role of BESS in grid services is equally crucial. These systems are adept at providing essential grid services such as load balancing and frequency regulation. Through rapid response capabilities, BESS can adjust to changes in electricity demand or supply, maintaining a stable grid frequency and preventing power outages. In demand response scenarios, BESS can be used to reduce the load on the grid during peak times, an invaluable tool in managing energy consumption and reducing costs.
Capacity markets
Utility-scale energy storage presents significant opportunities. Capacity markets are designed to ensure that there is sufficient energy generation capacity to meet peak demand. BESS can contribute to these markets by providing additional capacity when needed, acting as a buffer during times of high demand or generation shortfall. This not only improves grid reliability but also opens new revenue streams for operators of utility-scale energy storage systems. As these markets evolve, the strategic importance of BESS is expected to grow, further underlining their role as a key component in the future energy landscape.
United States of America
According to a recent report from Reuters (November 2023), the Biden administration's Inflation Reduction Act has catalysed energy storage development across the United States. Rising solar and wind capacity is increasing the need for battery storage and the inflation act includes investment tax credits (ITCs) for stand-alone storage facilities for the first time. Energy storage allows solar developers to capitalise on evening peak power prices or provide ancillary grid services and most new utility-scale solar projects include batteries.
Germany
In 2021, Germany's Federal Network Agency launched Innovation Tenders that provide developers with fixed premiums on energy injected onto the grid for a period of 20 years to encourage renewable-plus-storage deployment throughout the country. This tender is set to occur on an annual basis with an expected procurement of 5,450MW of total capacity by 2028. Battery storage systems must be charged from the renewable asset and need to have the ability to provide automatic Frequency Restoration Reserve services.
France
France's aFRR (automatic Frequency Restoration Reserve) recently opened, unlocking an additional source of revenue for battery storage projects across the country. The full potential of the aFRR will be unlocked further into 2024 with a possibility for battery storage receiving additional capacity revenue atop renewable energy. At the time of writing, less than 50MW of battery capacity has been certified to procure aFRR which makes for an attractive market opportunity.
Australia
Australia is leading the global market for forecasted BESS deployments, with the total pipeline of announced projects now exceeding 40 gigawatts (GW), according to latest Wood Mackenzie analysis. The surge in renewable energy has made Australia one of the most attractive markets for grid-scale energy storage globally. This has been helped by the presence of competitive wholesale and frequency control markets offering diverse revenue streams for battery storage, and significant funding from the Australian government providing revenue certainty to storage projects.
Asia-Pacific
Studies have shown that capacity avoidance or deferral is the biggest source of value for energy storage in the long run, especially in the Asia-Pacific region. Energy storage complements other fixed assets in the network and allows for better planning and operation of the network. The addition of storage can defer transmission upgrades as it can address the issue of congestion in the network by delivering power during periods of low use and more available capacity.
The competitive landscape and revenue stacking
Businesses eyeing investment in Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) face a competitive landscape that is both challenging and ripe with opportunities. This market is characterised by a mix of established energy storage primes and emerging innovative firms, all pushing the boundaries of storage technology. Investment viability hinges not only on technological prowess but also on market adaptability and scalability. Investors need to consider factors like technological reliability, cost-effectiveness, and the provider's ability to navigate complex regulatory environments.
Understanding the concept of revenue stacking in utility-scale BESS is crucial.
This strategy involves layering multiple revenue streams from a single investment to maximise returns. Key revenue streams include energy arbitrage (buying low and selling high), providing ancillary services like frequency regulation, and participating in capacity markets to ensure energy availability during peak demand.
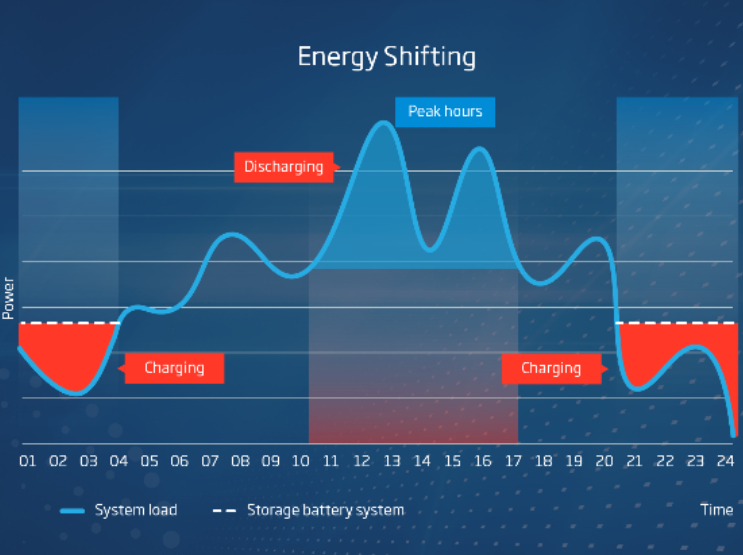
Additionally, engagement in demand response programs can yield additional financial benefits. Each of these streams represents a different facet of the value that a BESS can provide, making the investment not just about energy storage, but about versatile energy management. For businesses, this means a diversified investment portfolio with multiple avenues for return, enhancing the attractiveness and financial robustness of investing in BESS.
Conclusion
As energy infrastructure continues to evolve; it's supportive local policies and global sustainability trends that are driving the demand for Battery Energy Storage Systems. BESS integration with renewable sources like solar, their crucial role in grid services, and the emerging opportunities in capacity markets highlight the system's versatility and necessity that ultimately underpins the business case for energy storage.
Looking ahead, the future of energy storage is bright, with technological advancements and market growth. Trina Storage remains committed to leading this charge, innovating and expanding our solutions to meet the ever-growing energy demands sustainably and efficiently.
Relevant Topics
Smart Energy Solutions
delivered straight to your inbox

